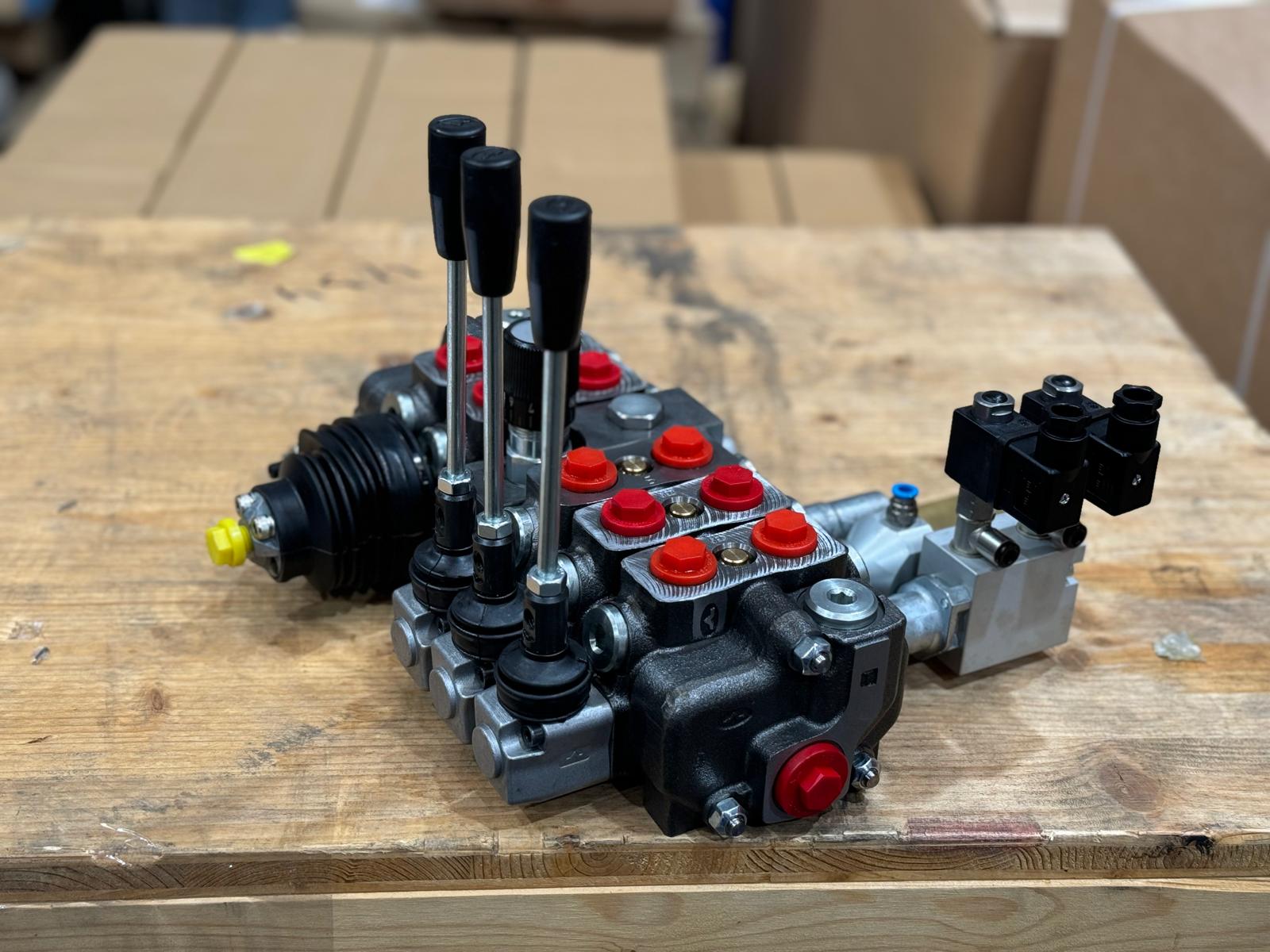
Hydraulic valves play a pivotal role in controlling fluid flow within a hydraulic system. Whether you're designing a new system or upgrading an existing one, selecting the right type of hydraulic valve is crucial for optimal performance and efficiency. Among the various types available, solenoid, manual, and proportional valves are widely used across different industries. In this blog we will look at the differences between these valve types, their applications, advantages, and considerations to help you make an informed decision when choosing the right hydraulic valve for your specific needs.
Understanding Hydraulic Valves:
Solenoid Valve: Solenoid valves are electromechanical devices that use an electric current to control the flow of fluid. They consist of a coil wound around a ferromagnetic core, which, when energized, creates a magnetic field that moves a plunger to open or close the valve.
Manual Valve: Manual valves, as the name suggests, are operated manually by an operator. They typically feature levers, knobs, or handles that allow users to adjust the flow of fluid manually. Manual valves are simple in design and offer precise control over fluid flow.
Proportional Valve: Proportional valves regulate fluid flow proportionally to an input signal, such as voltage or current. They offer precise control over flow rate, direction, and pressure and are often used in applications where fine control is required.
Now, let's compare these types of valves across various parameters:
Control:
Solenoid Valve: Solenoid valves provide on/off control, meaning they can only be fully open or fully closed.
Manual Valve: Manual valves offer manual control, allowing operators to adjust flow rates and direction as needed.
Proportional Valve: Proportional valves offer precise control over fluid flow, allowing for variable flow rates and direction proportional to the input signal.
Response Time:
Solenoid Valve: Solenoid valves typically have fast response times, making them suitable for applications requiring quick valve actuation.
Manual Valve: Response time depends on the operator, but manual valves generally have slower response times compared to solenoid valves.
Proportional Valve: Proportional valves have variable response times depending on the control signal and system parameters. They can offer both fast and slow response characteristics.
Accuracy:
Solenoid Valve: Solenoid valves provide accurate on/off control but may not offer precise flow control.
Manual Valve: Manual valves offer good accuracy when operated by experienced operators but may lack precision compared to proportional valves.
Proportional Valve: Proportional valves are known for their high accuracy and precise control over flow rates, direction, and pressure.
Energy Efficiency:
Solenoid Valve: Solenoid valves consume energy only when actuated, making them energy-efficient for on/off applications.
Manual Valve: Manual valves do not consume additional energy but rely on manual operation, which may not always be efficient.
Proportional Valve: Proportional valves can be energy-efficient when properly integrated into a system, as they adjust fluid flow based on demand.
Applications: Now, let's explore the typical applications where each type of hydraulic valve excels:
Solenoid Valve: Solenoid valves are commonly used in applications requiring on/off control, such as industrial automation, irrigation systems, and pneumatic systems.
Manual Valve: Manual valves find applications in scenarios where manual control is sufficient or preferred, such as hydraulic presses, manual override systems, and low-pressure hydraulic systems.
Proportional Valve: Proportional valves are ideal for applications requiring precise control over flow rates, direction, and pressure, including injection molding machines, aerospace systems, and hydraulic servo systems.
Considerations for Selection: When choosing the right hydraulic valve for your application, consider the following factors:
Application Requirements: Determine the specific requirements of your application, including flow rate, pressure, response time, and accuracy.
Control Strategy: Decide whether on/off control, manual control, or proportional control is needed based on the application's demands.
Energy Efficiency: Evaluate the energy consumption and efficiency of the valve type to ensure optimal performance and cost-effectiveness.
Integration: Consider how the valve will integrate into your existing hydraulic system and whether any additional components or modifications are necessary.
Maintenance: Assess the maintenance requirements of each valve type, including reliability, lifespan, and ease of servicing.
Choosing the right hydraulic valve—whether solenoid, manual, or proportional—is essential for achieving optimal performance and efficiency in hydraulic systems. Each type of valve offers distinct advantages and is suited to specific applications based on control requirements, response time, accuracy, energy efficiency, and other factors. By understanding the differences between these valve types and considering the unique needs of your application, you can make an informed decision that maximizes the performance and reliability of your hydraulic system.
At VHS Hydraulic Components we stock a wide range of hydraulic valves including:
Walvoil – Directional control valves, SD5,SD11,SD4, SD18
Walvoil – Manual + Electric solenoid diverters, DF/DFE
Brevini – Manual + Electric cetop 3 valves, ADB3E + AD3L
Bosch Rexroth – M4 Proportional load sensing valve, available with electric or manual control
To enquire or speak to our technical team about all your hydraulic solutions please contact VHS Hydraulic Components on: 0114 276 4430 / E: info@www.hydraulic-components.net or visit our website at: https://www.hydraulic-components.net





 No Minimum Order
No Minimum Order















